Introduction
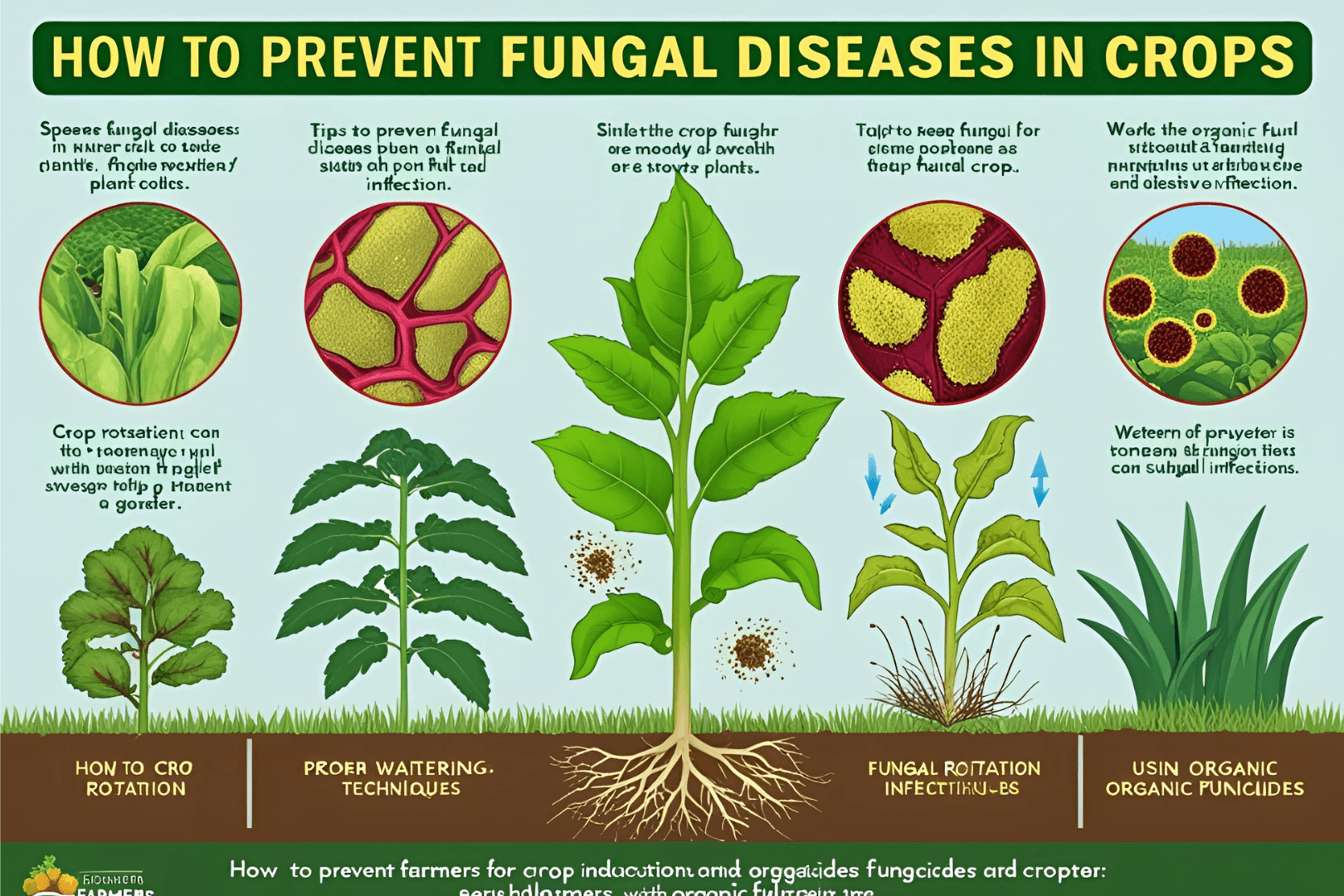
Fungal diseases pose a major threat to crop production, leading to reduced yields and significant financial losses for farmers. These diseases spread through spores in the air, soil, and water, affecting various parts of the plant, including leaves, stems, and roots. However, with proper preventive measures, farmers can effectively minimize fungal infections and maintain healthy crops.
1. Choose Disease-Resistant Varieties
- Select crop varieties that are naturally resistant to common fungal diseases.
- Government agricultural research institutes and seed companies develop disease-resistant seeds for crops like wheat, rice, and vegetables.
- Certified disease-free seeds reduce the risk of fungal infections from the start.
2. Practice Crop Rotation
- Avoid planting the same crop in the same field season after season.
- Rotating crops like legumes, cereals, and vegetables helps break the life cycle of fungal pathogens.
- Crop rotation improves soil health and reduces the buildup of disease-causing fungi.
3. Ensure Proper Field Drainage
- Waterlogged soil creates ideal conditions for fungal growth.
- Implement proper drainage systems such as raised beds, contour farming, and irrigation scheduling.
- Avoid excessive watering to prevent root rot and damping-off diseases.
4. Maintain Proper Plant Spacing
- Overcrowded plants create humid conditions, encouraging fungal growth.
- Follow recommended spacing guidelines to improve air circulation and reduce moisture buildup.
- Prune excess leaves to allow sunlight penetration and faster drying of foliage.
5. Use Organic and Natural Fungicides
- Apply neem oil, copper sulfate, or sulfur-based sprays to prevent fungal infections.
- Prepare homemade sprays using garlic extract, baking soda, or cow urine to deter fungal spores.
- Use Trichoderma fungi as a biocontrol agent to suppress harmful fungal pathogens in the soil.
6. Apply Mulching for Soil Protection
- Use organic mulch like straw, dry leaves, or wood chips to prevent fungal spores from splashing onto plants.
- Mulching maintains soil moisture balance and reduces weed growth, which can harbor fungal diseases.
- Avoid thick layers of wet mulch, as it may promote fungal infections.
7. Sanitize Farming Tools & Equipment
- Regularly disinfect farm tools, seed trays, and irrigation pipes to prevent disease spread.
- Avoid using infected plant residues as compost without proper decomposition.
- Clean hands, boots, and machinery when moving between fields to prevent cross-contamination.
8. Monitor Weather Conditions
- Fungal diseases spread rapidly in warm, humid, and rainy conditions.
- Use weather apps and agricultural advisory services to track disease-prone weather patterns.
- Plan fungicide applications before expected rain or humidity spikes.
9. Control Weeds and Remove Infected Plants
- Weeds can act as hosts for fungal diseases. Regular weeding reduces disease risks.
- Remove and destroy infected plants immediately to prevent fungal spores from spreading.
- Never leave diseased plant debris in the field; burn or compost it properly.
10. Proper Soil Management & Nutrient Balance
- Maintain soil health by adding organic matter like compost and farmyard manure.
- Use balanced fertilizers—excess nitrogen can make plants more susceptible to fungal attacks.
- Conduct soil testing to identify deficiencies and apply appropriate amendments.
Conclusion
Preventing fungal diseases requires a combination of good agricultural practices, timely monitoring, and natural remedies. By implementing these preventive measures, farmers can ensure healthy crops, minimize yield losses, and reduce dependency on chemical fungicides.
📞 For Fungal Disease Prevention Assistance
📧 ratanmetalsjaipur@gmail.com
📞 +91 7014180458
Stay proactive in protecting your crops from fungal infections! 🌱🚜